Office
Office
 Issue
Issue
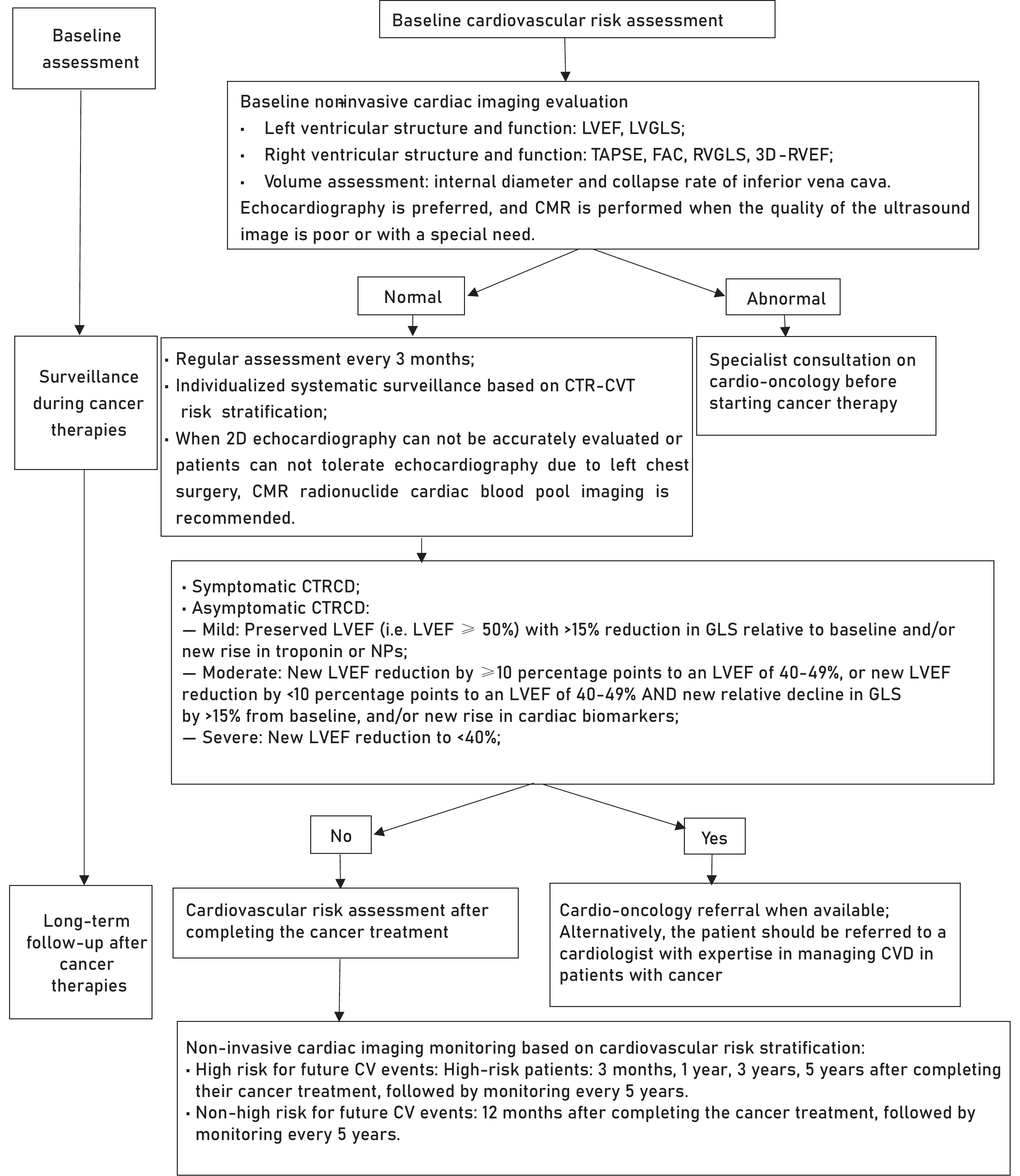
Cardiovascular damage caused by cancer treatment has become an important cause of death for tumor survivors. With the recognition of cardiovascular diseases and cancer therapy-related cardiovascular toxicity (CTR-CVT) in tumor patients, noninvasive imaging technologies play pivotal roles in the risk stratification, early diagnosis, monitoring and follow-up for CTR-CVT. In recent years, the field of cardio-oncology has witnessed continual updates in diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, with several pertinent guidelines and expert consensus documents issued in China and abroad. However, there remains a conspicuous absence of systematic guidance documents on the application of imaging techniques in the clinical practice of cardio-oncology. Therefore, the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Society of Integrative Cardio-oncology, the Ultrasound Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, and the Chinese Society of Echocardiography convened experts to formulate the "Chinese guideline for the clinical application of noninvasive imaging technology in accessing cancer therapy-related cardiovascular toxicity". Building upon the systematic evaluation of guidelines and the latest evidence-based medical research in the field of cardio-oncology domestically and abroad, and in conjunction with data derived from evidence-based medical research in China, this guideline proposes noninvasive imaging examination methods and monitoring strategies for CTR-CVT, aiming to further standardize and guide the clinical practice of multidisciplinary physicians specializing in cardio-oncology in China.
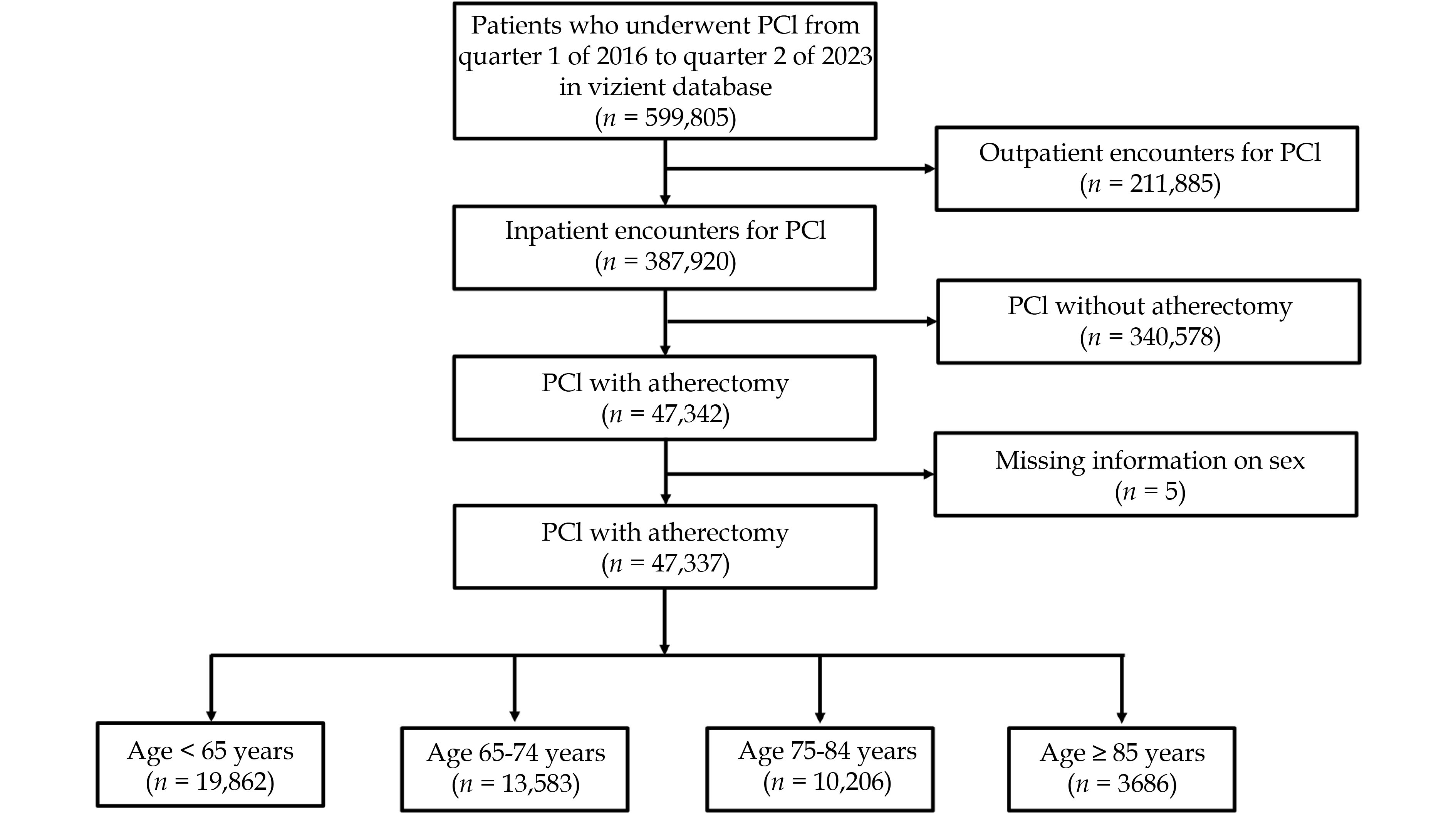
Coronary atherectomy is used to treat severely calcified coronary artery lesions which are more frequent with increasing age, but its impact in older adults has not been sufficiently examined.
We compared adults ≥ 18 years old who underwent coronary atherectomy during inpatient PCI in 2016–2023 from the Vizient Clinical Data Base and compared outcomes in younger (< 65 years), youngest-old (65–74 years), middle-old (75–84 years), and oldest-old (≥ 85 years) adults. Primary outcome was in-hospital mortality, and secondary outcomes included postprocedural complications.
Among 47,337 patients who underwent coronary atherectomy, 19,862 (42.0%) were younger adults and 27,475 (58.0%) were older adults, including 13,583 youngest-old, 10,206 middle-old, and 3,686 oldest-old adults. Compared with younger adults, youngest-old adults had higher mortality (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] = 1.37, P < 0.001), ischemic stroke (aOR = 1.35, P = 0.005), gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIH) (aOR = 1.44, P < 0.001), acute kidney injury (AKI) (aOR = 1.43, P < 0.001), tamponade (aOR = 1.86, P < 0.001), and pericardiocentesis (aOR = 2.32, P < 0.001). Middle-old adults had higher mortality (aOR = 1.80, P < 0.001), GIH (aOR = 1.42, P = 0.002), AKI (aOR = 1.63, P < 0.001), tamponade (aOR = 2.52, P < 0.001), and pericardiocentesis (aOR = 3.13, P < 0.001). Oldest-old adults had the highest odds for mortality (aOR = 2.03, P < 0.001), GIH (aOR = 1.48, P = 0.016), AKI (aOR = 2.26, P < 0.001), tamponade (aOR = 3.86, P < 0.001), and pericardiocentesis (aOR = 4.21, P < 0.001). There was a significant interaction (P-interaction=0.035) between atherectomy and age groups with regard to the odds of in-hospital mortality.
In this large claims-based study, in-hospital mortality, GIH, AKI, tamponade, and pericardiocentesis were higher in older adults compared with younger adults, in a stepwise manner by age group.
The number of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) procedures in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS) is increasing worldwide. We aimed to assess the impact of a TAVI program on clinical profile, management and outcomes of these patients and to describe predictors of length of hospital stay (LoS) in this context.
Retrospective single center study enrolling consecutive AS patients undergoing TAVI and surviving to discharge (January 2018-December 2022). A TAVI program was implemented in may 2021. Baseline clinical characteristics, management and in-hospital complications were registered. Predictors of long hospital stay (> 7 day) were assessed by binary logistic regression.
We included 614 patients, with mean age 80.5 years. Most patients (438/614, 71.2%) presented conditions that precluded an early discharge. Mean hospital stay was 7.6 days. Patients admitted after the implementation of the program had a significantly lower burden of comorbidities. The rate of conduction disturbances after TAVI remained stable around 60%. However, permanent pacemaker requirement declined from 30.3% to 22.5% (P = 0.028). LoS was reduced after the implementation of the program both in patients suitable for an early discharge (from 6.5 day to 4 day, P < 0.001) and unsuitable patients (from 9.4 day to 7.7 day, P = 0.014). The final predictive model for LoS included prior pacemaker and availability of TAVI program as protectors and other valvular diseases, day of the week, emergent procedures, and conduction disturbances and other complications as independent predictors of long stay after TAVI.
Most patients undergoing TAVI present conditions that preclude an early hospital discharge. The implementation of a TAVI program improved selection of patients, with a lower burden of comorbidities, a lower rate of complications and a marked reduction of hospital stay.
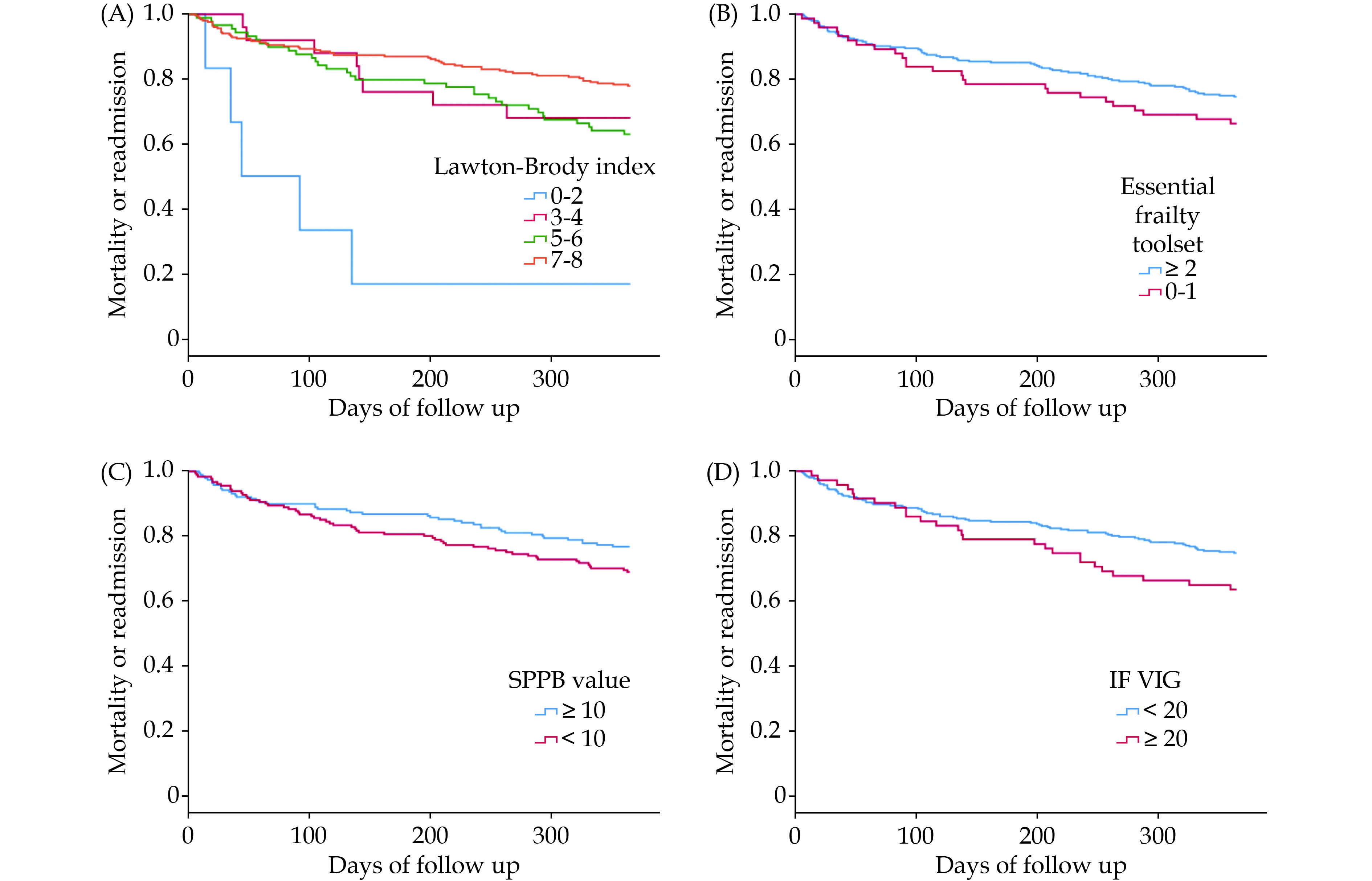
There is scarce data about comparisons between geriatric assessment tools in patients with aortic stenosis (AS). We aimed to describe the geriatric profile of patients with AS undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) and to analyze the ability of different tools for predicting clinical outcomes in this context.
This was a single center retrospective registry including patients with AS undergoing TAVI and surviving to hospital discharge. The primary endpoint was all-cause mortality or need for urgent readmission one year after TAVI.
A total of 377 patients were included (mean age of 80.4 years). Most patients were independent or mildly dependent, with an optimal cognitive status. The proportion of frailty ranged from 17.6% to 49.8%. A total of 20 patients (5.3%) died and 110/377 patients (29.2%) died or were readmitted during follow up. Overall, most components of the geriatric assessment showed an association with clinical outcomes. Disability for instrumental activities showed a significant association with mortality and a strong association with the rate of mortality or readmission. The association between frailty and clinical outcomes was higher for short physical performance battery (SPPB), essential frailty toolset (EFT) and the frailty index based on comprehensive geriatric assessment (IF-VIG) and lower for Fried criteria and FRAIL scale.
AS patients from this series presented a good physical performance, optimal cognitive status and a reasonably low prevalence of frailty. The best predictive ability was observed for disability for instrumental activities and frailty as measured by the EFT, SPPB and the IF-VIG.
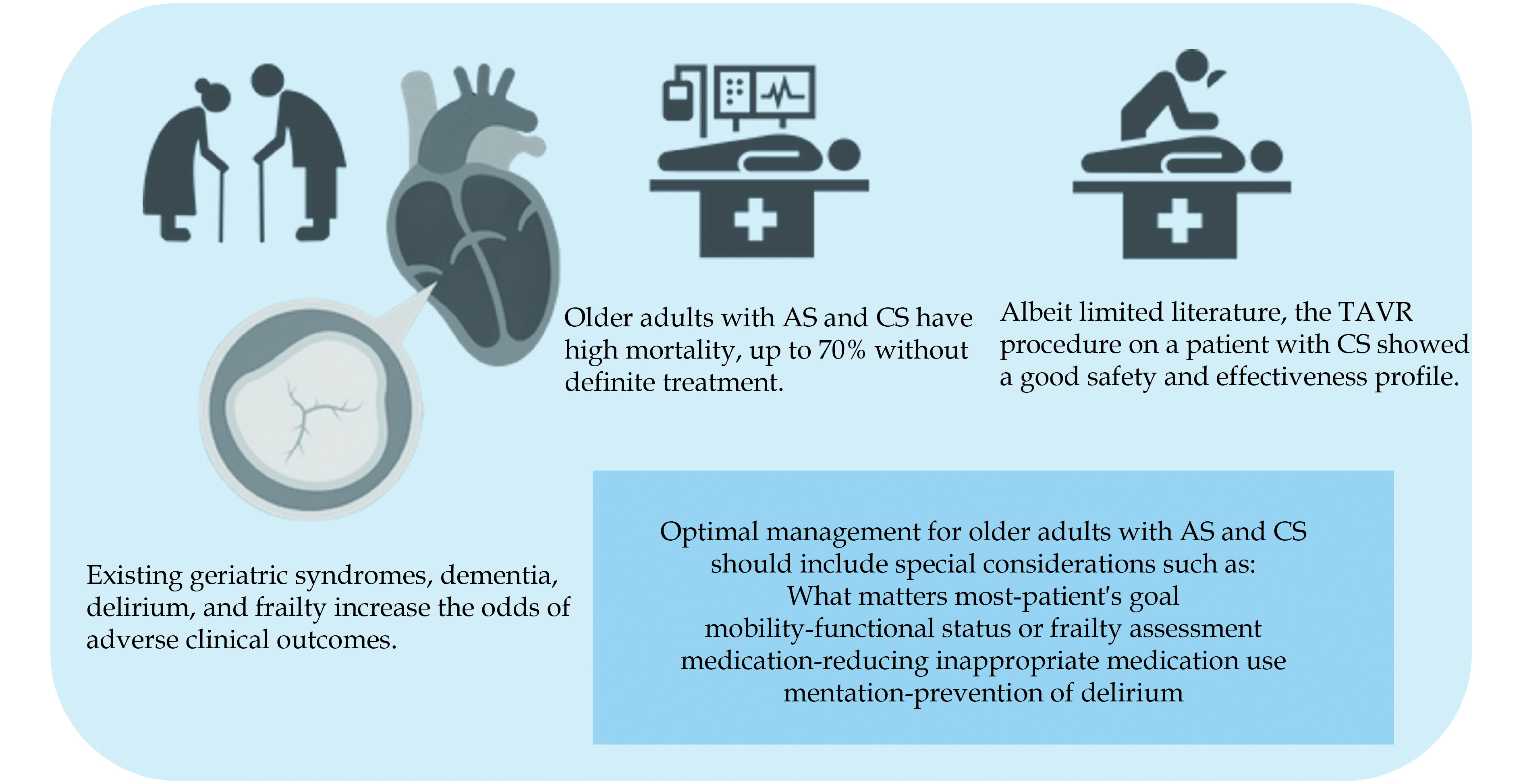
Aortic stenosis (AS) is one of the most common types of valvular heart disease in older adults, with age being significantly associated with the development of AS. The transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) procedure, since it was first performed in 2002, has emerged as a preferred treatment option for patients who are at intermediate to high surgical risk due to advanced age or medical comorbidities. Older adults with severe AS may present with acute decompensated heart failure leading to cardiogenic shock (CS). Among patients 65 years and older with AS presenting for TAVR, 4.1% were reportedly in acute CS. Regardless of etiology, mortality from CS itself is high (30%−50%) and increases with advancing age. TAVR for these patients could provide a definite treatment for both AS and CS. There is still limited evidence regarding the safety and efficacy of TAVR in this population, but recent studies are promising, with successful procedural results and a good recovery rate after the procedure. However, particularly for older adults, there are other factors that clinicians should consider during pre- and post-procedural status, such as patient’s goals, frailty, polypharmacy, dementia, or delirium. In this article, we reviewed current studies regarding TAVR for older adults with AS and CS, the reason for comprehensive geriatric assessment, and the introduction of appropriate geriatric assessment tools based on the Age-Friendly 4Ms framework that cardiologists can adopt in real-world practice.
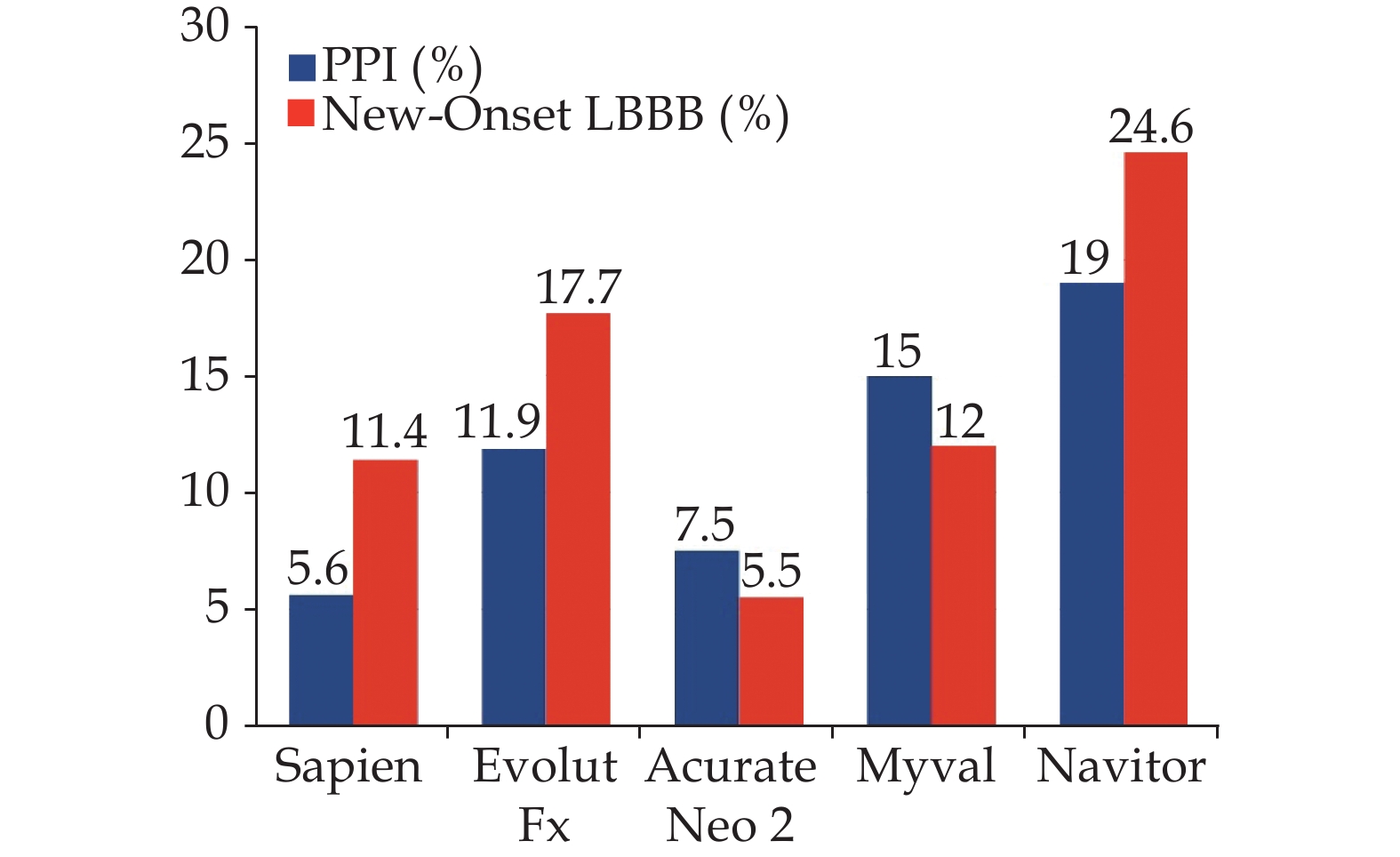
The incidence of new-onset cardiac conduction disturbances following transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has not decreased compared to other complications, and nowadays is by far the most frequent drawback following the procedure. Meanwhile, the global management of TAVI recipients has led to a minimalist approach with short postprocedural length of stay, which may be limited by the occurrence of late arrhythmic events in patients at high-risk. This review focuses on those strategies to overcome the conundrum between early discharge and new-onset conduction disturbances in elderly TAVI candidates and provides a perspective on future improvements in this field.
 First
First
 News
News